Proteins are the building blocks of life, and understanding their structure and function is essential to unlocking the mysteries of biology and medicine. However, not all proteins function as they should, and unfolded proteins play a critical role in various biological processes and diseases. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of unfolded proteins, exploring their significance, causes, effects, and potential solutions.
This guide aims to provide readers with an in-depth understanding of unfolded proteins, their role in health and disease, and the latest advancements in research. Whether you're a student, scientist, or simply curious about the science behind protein folding, this article will serve as a valuable resource.
By the end of this article, you'll gain insights into how unfolded proteins impact cellular function, their association with diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, and the cutting-edge technologies being developed to combat these issues. Let's dive in!
Read also:Is Ynw Melly Still Alive Unveiling The Truth Behind The Rumors
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Unfolded Proteins
- Understanding Protein Structure and Function
- What Are Unfolded Proteins?
- Causes of Protein Unfolding
- Effects of Unfolded Proteins on Cellular Function
- Unfolded Proteins and Disease
- Diagnosis of Unfolded Protein-Related Disorders
- Prevention and Management Strategies
- Emerging Technologies for Protein Folding
- The Future of Unfolded Protein Research
- Conclusion
Introduction to Unfolded Proteins
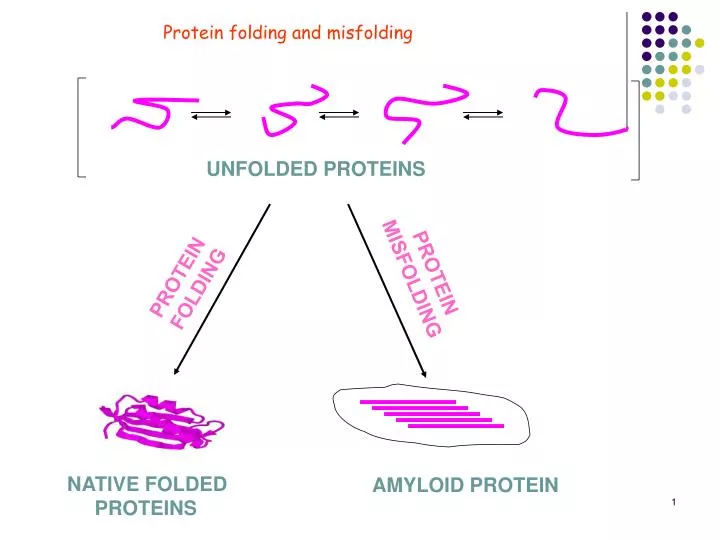
Proteins are complex molecules that perform a wide range of functions within living organisms. They are responsible for everything from catalyzing metabolic reactions to providing structural support. However, proteins must fold into specific three-dimensional shapes to function correctly. When proteins fail to fold properly, they become unfolded proteins, which can lead to serious consequences for cellular health.
Unfolded proteins are not just a scientific curiosity; they are a critical area of study in modern biology and medicine. Understanding the mechanisms behind protein unfolding and misfolding can provide insights into a variety of diseases and disorders, including neurodegenerative conditions, cancer, and metabolic disorders.
Understanding Protein Structure and Function
Before diving into the world of unfolded proteins, it's essential to grasp the basics of protein structure and function. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are linked together in a specific sequence determined by the genetic code. This sequence determines the primary structure of the protein.
From the primary structure, proteins fold into secondary structures, such as alpha-helices and beta-sheets, and then into tertiary structures, which represent the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein. Some proteins also form quaternary structures when multiple polypeptide chains come together.
Key Functions of Proteins
- Enzymes: Catalyze biochemical reactions.
- Structural Proteins: Provide support and structure, such as collagen and keratin.
- Transport Proteins: Carry molecules like hemoglobin, which transports oxygen.
- Signaling Proteins: Facilitate communication between cells, such as hormones.
What Are Unfolded Proteins?
Unfolded proteins refer to proteins that have not achieved their functional three-dimensional structure. These proteins lack the specific conformation required to perform their intended biological roles. Unfolded proteins can result from errors during the folding process or environmental factors that disrupt the protein's stability.
In some cases, unfolded proteins can refold into their functional state with the help of molecular chaperones. However, if the unfolding persists, it can lead to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, which may aggregate and cause cellular damage.
Read also:Unveiling The Truth About Malachi Jakes Biological Father
Causes of Protein Unfolding
Several factors can lead to protein unfolding, including:
- Mutations: Genetic mutations can alter the amino acid sequence of a protein, affecting its ability to fold correctly.
- Environmental Stress: High temperatures, pH changes, and oxidative stress can disrupt protein folding.
- Post-Translational Modifications: Modifications such as phosphorylation or glycosylation can influence protein folding.
- Defective Chaperones: Molecular chaperones assist in protein folding, and their malfunction can lead to protein misfolding.
Effects of Unfolded Proteins on Cellular Function
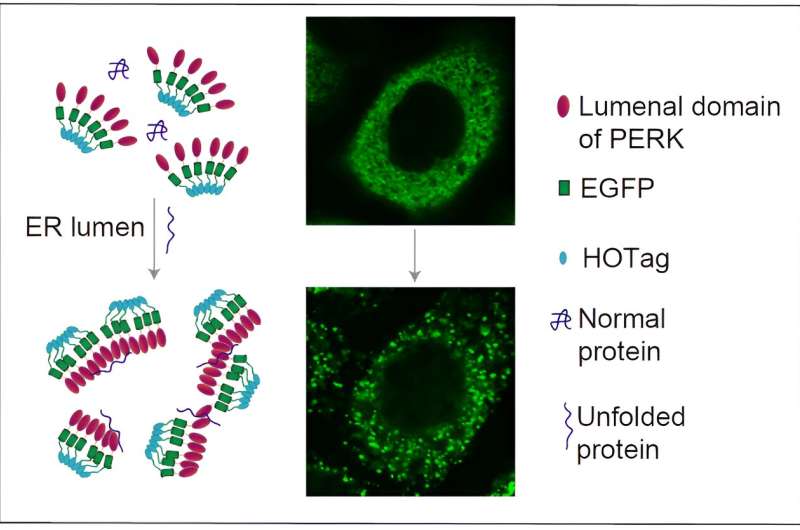
Unfolded proteins can have profound effects on cellular function. When proteins fail to fold properly, they may lose their functionality, leading to impaired cellular processes. Additionally, unfolded proteins can aggregate, forming toxic protein clumps that disrupt cellular homeostasis.
Cells have developed mechanisms to deal with unfolded proteins, such as the unfolded protein response (UPR). The UPR aims to restore protein folding balance by increasing the production of chaperones and reducing protein synthesis. However, if the UPR fails, it can trigger apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
Unfolded Proteins and Disease
The accumulation of unfolded proteins is associated with a range of diseases, particularly those involving protein aggregation. Below, we explore two major categories of diseases linked to unfolded proteins: neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's are characterized by the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the brain. For example, in Alzheimer's disease, the aggregation of beta-amyloid peptides and tau proteins leads to the formation of plaques and tangles, which damage neurons.
Research into these diseases focuses on understanding the mechanisms of protein misfolding and developing therapies to prevent or reverse the aggregation process.
Cancer
In cancer, unfolded proteins can contribute to tumor development and progression. Cancer cells often experience high levels of stress due to rapid growth and division, leading to protein misfolding. The UPR in cancer cells can promote survival and drug resistance, making it a target for cancer therapy.
Diagnosis of Unfolded Protein-Related Disorders
Diagnosing disorders related to unfolded proteins involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging techniques. Biomarkers for misfolded proteins, such as beta-amyloid and tau in Alzheimer's disease, are increasingly being used for early detection.
Advances in proteomics and imaging technologies, such as cryo-electron microscopy, are providing deeper insights into protein structure and misfolding processes, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of these disorders.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing and managing disorders associated with unfolded proteins involves a multifaceted approach. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacological interventions, including drugs that target protein aggregation or enhance the UPR, are also under development.
In addition, gene therapy and immunotherapy offer promising avenues for treating diseases linked to protein misfolding. These therapies aim to restore normal protein folding or eliminate toxic protein aggregates.
Emerging Technologies for Protein Folding
Recent advancements in biotechnology have revolutionized our understanding of protein folding and misfolding. Technologies such as:
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy: Allows for high-resolution imaging of protein structures.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms predict protein folding patterns and identify potential drug targets.
- High-Throughput Screening: Facilitates the discovery of compounds that stabilize protein folding.
These technologies are paving the way for more effective treatments and therapies targeting unfolded proteins.
The Future of Unfolded Protein Research
The study of unfolded proteins is a rapidly evolving field with significant implications for human health. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of protein folding and misfolding, new opportunities for therapeutic intervention will emerge.
Future directions include the development of personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored to an individual's specific protein folding issues. Additionally, collaborations between scientists, clinicians, and technology developers will be crucial in advancing our understanding of unfolded proteins and their role in disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding unfolded proteins is vital for unraveling the mysteries of biology and medicine. From their role in cellular function to their association with diseases, unfolded proteins represent a fascinating area of scientific inquiry. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of unfolded proteins, their causes, effects, and potential solutions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your knowledge of biology and medicine. Together, we can continue to advance our understanding of the intricate world of proteins and their impact on human health.