The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Volatility Index And Its Role In Financial Markets
Mar 19 2025
Volatility index, commonly known as the VIX, is a critical financial tool that measures market expectations of near-term volatility based on options pricing. It provides traders and investors with valuable insights into the market's sentiment and potential future price movements. As a benchmark for market volatility, the VIX plays a pivotal role in shaping investment strategies and risk management decisions.
The financial markets are inherently unpredictable, with prices fluctuating due to a wide range of factors, including economic data, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment. In this complex environment, understanding the volatility index is essential for navigating the uncertainties of the market. By analyzing the VIX, investors can better anticipate market conditions and make informed decisions.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the volatility index, exploring its origins, significance, and applications. We'll also examine how the VIX can be leveraged to enhance investment strategies, manage risks, and capitalize on market opportunities. Whether you're a seasoned trader or a beginner, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to understand and utilize the volatility index effectively.
Read also:Joyymei Tape A Comprehensive Exploration Of The Phenomenon
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to the Volatility Index
- History of the Volatility Index
- How the Volatility Index is Calculated
- Interpreting Volatility Index Values
- The Volatility Index and Market Sentiment
- Volatility Index Trading Strategies
- Volatility Index as a Risk Management Tool
- Volatility Index ETFs and Futures
- Criticisms and Limitations of the Volatility Index
- Conclusion
Introduction to the Volatility Index
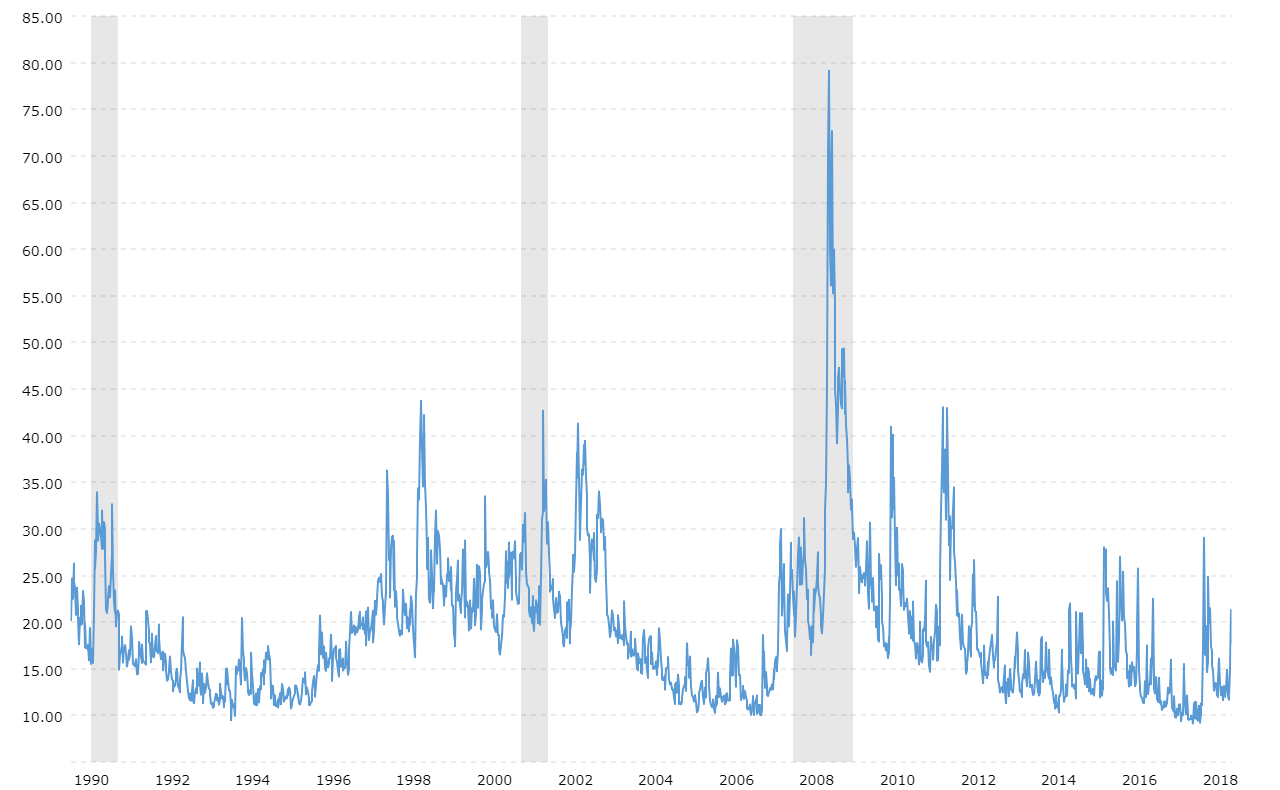
The volatility index, or VIX, is a widely recognized financial metric that gauges the level of volatility expected in the market over the next 30 days. It is often referred to as the "fear gauge" because it reflects the degree of uncertainty or fear among investors. Developed by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the VIX is derived from the prices of S&P 500 index options.
Why is the Volatility Index Important?
The VIX serves as a key indicator for assessing market conditions and predicting potential price movements. By monitoring the VIX, traders and investors can gain insights into market sentiment, which helps in making informed decisions. A rising VIX typically indicates increased market volatility and uncertainty, while a declining VIX suggests stability and calmness.
Applications of the Volatility Index
- Investment strategy formulation
- Risk management
- Portfolio diversification
- Market trend analysis
History of the Volatility Index
The VIX was introduced by the CBOE in 1993 as a way to measure market volatility. Initially, it was based on the S&P 100 index, but in 2003, it was recalibrated to reflect the broader S&P 500 index. This change enhanced its relevance and accuracy in gauging market expectations.
Evolution of the VIX
Over the years, the VIX has evolved to incorporate more sophisticated methodologies and data sources. Advances in technology and financial modeling have improved its precision and reliability. Today, the VIX is a cornerstone of modern financial analysis and a critical tool for traders and investors.
How the Volatility Index is Calculated
The VIX is calculated using a complex formula that involves the prices of S&P 500 index options. It takes into account the implied volatility of these options, which reflects the market's expectations of future price movements. The calculation process involves several steps, including:
Read also:Sarah Jakes Roberts Age Difference A Comprehensive Exploration
- Collecting data on S&P 500 options prices
- Estimating implied volatility
- Aggregating the data to produce a single volatility index value
Key Factors in VIX Calculation
Several factors influence the VIX calculation, including:
- Time to expiration of options
- Strike prices of options
- Market demand for options
Interpreting Volatility Index Values
Understanding the VIX values is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Generally, a VIX value below 20 indicates low volatility and market stability, while a value above 30 suggests high volatility and uncertainty. However, these thresholds can vary depending on market conditions and investor sentiment.
Significance of VIX Levels
Investors often use the VIX as a barometer for market sentiment. A rising VIX may signal increasing fear and uncertainty, prompting investors to adopt more conservative strategies. Conversely, a declining VIX may indicate growing confidence and optimism, encouraging more aggressive investment approaches.
The Volatility Index and Market Sentiment
The VIX is closely linked to market sentiment, reflecting the collective emotions and expectations of investors. By analyzing the VIX, traders can gain insights into the prevailing market mood and adjust their strategies accordingly. This relationship between the VIX and market sentiment is a key aspect of modern financial analysis.
How Market Sentiment Affects the VIX
Market sentiment can significantly impact the VIX, as investor emotions and expectations influence option prices. During periods of heightened uncertainty, such as economic recessions or geopolitical crises, the VIX tends to rise, reflecting increased volatility and risk.
Volatility Index Trading Strategies
Traders use various strategies to capitalize on the VIX's fluctuations. These strategies include options trading, futures trading, and ETF investing. By leveraging the VIX, traders can hedge against market risks and enhance their portfolio performance.
Popular VIX Trading Strategies
- VIX options trading
- VIX futures trading
- VIX ETF investing
Volatility Index as a Risk Management Tool
The VIX plays a vital role in risk management, helping investors mitigate potential losses and protect their portfolios. By incorporating the VIX into their risk management strategies, investors can better navigate market uncertainties and achieve their financial goals.
Implementing VIX in Risk Management
Investors can use the VIX to:
- Identify potential market risks
- Adjust portfolio allocations
- Hedge against market volatility
Volatility Index ETFs and Futures
VIX ETFs and futures provide traders and investors with additional tools to manage market volatility. These financial instruments allow investors to gain exposure to the VIX without directly trading options. Popular VIX ETFs include the iPath S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures ETN and the ProShares VIX Short-Term Futures ETF.
Advantages of VIX ETFs and Futures
- Liquidity
- Flexibility
- Cost-effectiveness
Criticisms and Limitations of the Volatility Index
While the VIX is a valuable tool for analyzing market volatility, it has its limitations. Critics argue that the VIX may not always accurately reflect market conditions, especially during extreme market events. Additionally, the VIX's reliance on options pricing can lead to discrepancies between its value and actual market volatility.
Addressing VIX Limitations
To overcome these limitations, investors should use the VIX in conjunction with other financial metrics and tools. By adopting a comprehensive approach to market analysis, investors can enhance their understanding of market dynamics and improve their decision-making processes.
Conclusion
The volatility index, or VIX, is an indispensable tool for navigating the complexities of the financial markets. By understanding its origins, significance, and applications, investors can harness the power of the VIX to enhance their investment strategies and manage risks effectively. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the VIX will remain a cornerstone of modern financial analysis and decision-making.
We encourage you to explore the VIX further and incorporate it into your investment strategies. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights into the world of finance.