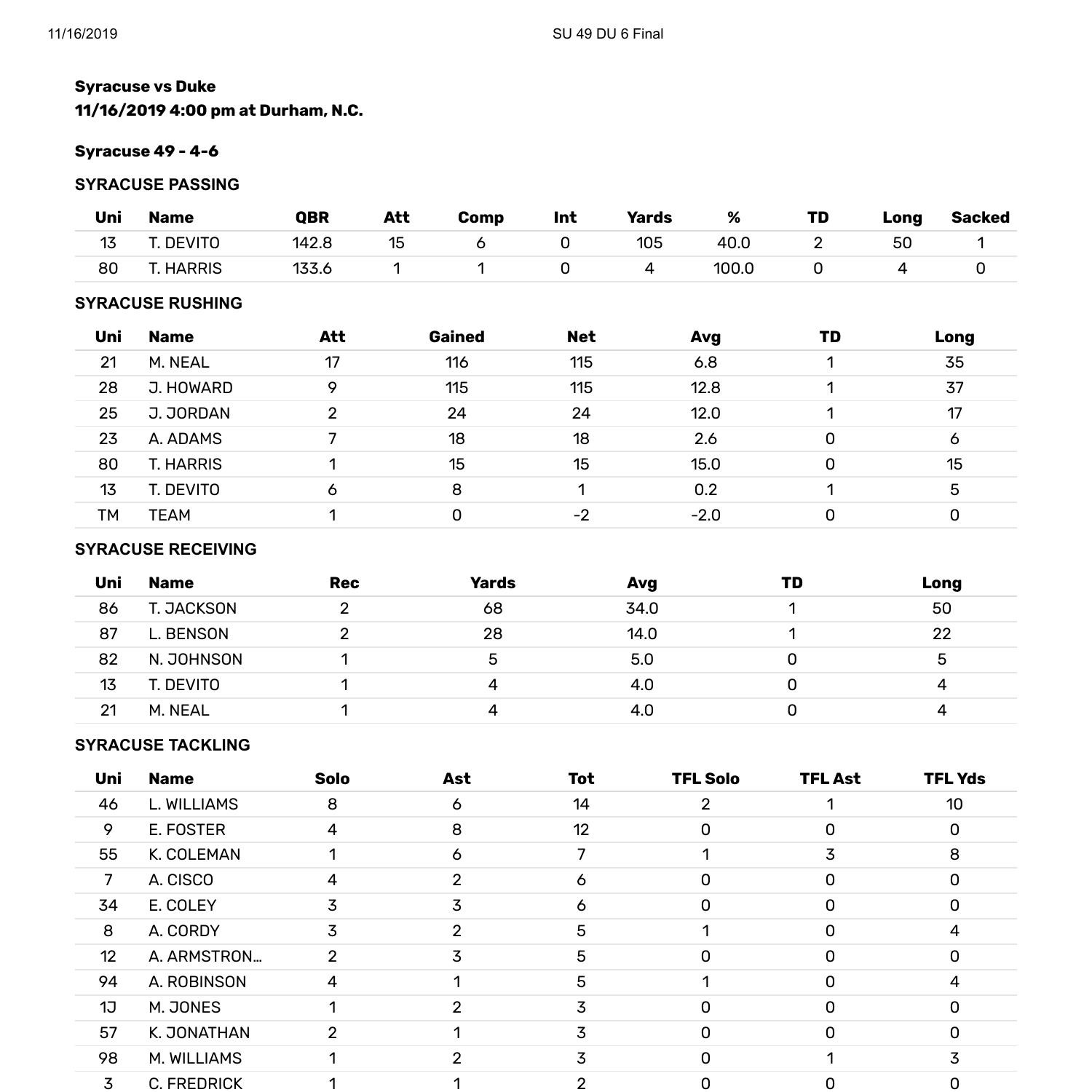
Cardiac risk assessment plays a crucial role in modern healthcare, and the Duke Score has emerged as a vital tool for evaluating potential cardiac issues in patients. This metric, widely used by healthcare professionals, helps in predicting the likelihood of coronary artery disease based on specific factors. Understanding the Duke Score is essential for both medical practitioners and individuals seeking to manage their heart health effectively.
The concept of Duke Score may seem complex at first glance, but it is a straightforward yet powerful tool in the medical field. By analyzing exercise capacity, angina symptoms, and stress test results, the Duke Score provides a numerical value that indicates the risk of coronary artery disease. This article aims to demystify the Duke Score, making it accessible for everyone interested in heart health.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the origins, applications, and significance of the Duke Score in modern medicine. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a student, or simply someone curious about heart health, this article will provide you with comprehensive insights into this essential diagnostic tool.
Read also:Catherine Mooty Children Exploring The Life And Legacy Of A Remarkable Woman
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Duke Score
- History of Duke Score
- Components of Duke Score
- How to Calculate Duke Score
- Duke Score and Cardiac Risk Assessment
- Clinical Applications
- Limitations of Duke Score
- Duke Score in Modern Medicine
- Future Perspectives
- Conclusion
Introduction to Duke Score
The Duke Score is a widely recognized metric used in cardiology to assess the risk of coronary artery disease. Developed in the late 20th century, this scoring system has become an integral part of cardiac diagnostics. It combines three critical factors: exercise capacity, angina symptoms, and the results of a stress test. By evaluating these components, healthcare professionals can predict the likelihood of coronary artery disease with reasonable accuracy.
Why Duke Score Matters
The importance of the Duke Score lies in its ability to provide a numerical value that reflects a patient's cardiac health. This score helps doctors make informed decisions regarding treatment plans and interventions. For patients, understanding their Duke Score can empower them to take proactive steps in managing their heart health.
History of Duke Score
The Duke Score was developed in the 1980s by researchers at Duke University Medical Center. Initially designed as a tool for stress test interpretation, it quickly gained recognition for its effectiveness in predicting coronary artery disease. Over the years, numerous studies have validated its reliability, leading to its widespread adoption in clinical practice.
Key Milestones in Duke Score Development
- 1980s: Initial development at Duke University
- 1990s: Validation through large-scale studies
- 2000s: Integration into standard cardiac diagnostic protocols
Components of Duke Score
The Duke Score is calculated based on three primary components:
- Exercise Capacity: Measured in metabolic equivalents (METs), this factor assesses how much physical activity a patient can perform during a stress test.
- Angina Symptoms: Categorized as absent, present, or present with ischemia, this component evaluates the presence and severity of chest pain during exercise.
- Stress Test Results: Indicates whether there is evidence of myocardial ischemia during the test.
How Each Component Contributes
Each component is assigned a numerical value, which is then summed to produce the final Duke Score. A higher score indicates a greater risk of coronary artery disease.
How to Calculate Duke Score
Calculating the Duke Score involves a straightforward formula:
Read also:Patricia Neal The Legendary Actress Who Left An Indelible Mark On Hollywood
Duke Score = Exercise Capacity (in METs) - 5 x Angina Symptoms + 4 x Stress Test Results
For example, if a patient achieves 8 METs, experiences angina symptoms (scored as 1), and has positive stress test results (scored as 1), their Duke Score would be:
Duke Score = 8 - (5 x 1) + (4 x 1) = 7
Practical Example
Let's consider another scenario. A patient achieves 10 METs, has no angina symptoms (scored as 0), and has negative stress test results (scored as 0). Their Duke Score would be:
Duke Score = 10 - (5 x 0) + (4 x 0) = 10
Duke Score and Cardiac Risk Assessment
The Duke Score plays a crucial role in cardiac risk assessment by providing a quantitative measure of a patient's risk for coronary artery disease. This information is invaluable for tailoring treatment plans and interventions to individual patient needs.
Interpreting Duke Score Results
Duke Score results can be interpreted as follows:
- Score ≤ 4: Low risk of coronary artery disease
- Score 5-8: Intermediate risk of coronary artery disease
- Score ≥ 9: High risk of coronary artery disease
Clinical Applications
The Duke Score is widely used in clinical settings for various purposes, including:
- Predicting the need for coronary angiography
- Guiding treatment decisions for patients with suspected coronary artery disease
- Monitoring disease progression over time
Case Studies
Several case studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the Duke Score in clinical practice. For instance, a study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that patients with high Duke Scores were significantly more likely to benefit from invasive interventions compared to those with low scores.
Limitations of Duke Score
While the Duke Score is a valuable tool, it does have certain limitations:
- It may not be accurate for all patient populations, especially those with atypical presentations of coronary artery disease.
- It relies heavily on the accuracy of stress test results, which can be influenced by various factors.
- It does not account for other risk factors such as family history or lifestyle factors.
Addressing Limitations
To overcome these limitations, healthcare professionals often use the Duke Score in conjunction with other diagnostic tools and patient-specific information. This holistic approach ensures a more comprehensive assessment of cardiac risk.
Duke Score in Modern Medicine
In modern medicine, the Duke Score continues to evolve alongside advancements in diagnostic technology. With the advent of new imaging techniques and biomarkers, the Duke Score remains a cornerstone of cardiac risk assessment. Its adaptability and reliability have ensured its relevance in contemporary healthcare.
Integration with Technology
The integration of the Duke Score with electronic health records and artificial intelligence systems has further enhanced its utility. These technologies allow for real-time analysis and interpretation of Duke Score results, improving patient care and outcomes.
Future Perspectives
The future of the Duke Score looks promising, with ongoing research exploring its potential applications in personalized medicine. As our understanding of cardiovascular disease continues to grow, the Duke Score is likely to play an even more significant role in cardiac diagnostics.
Potential Enhancements
Future enhancements may include:
- Incorporating genetic markers into the scoring system
- Developing algorithms that account for a wider range of risk factors
- Enhancing predictive accuracy through machine learning
Conclusion
The Duke Score is an indispensable tool in cardiac risk assessment, providing valuable insights into a patient's likelihood of developing coronary artery disease. By understanding its components, applications, and limitations, healthcare professionals and patients alike can make informed decisions about heart health. We encourage readers to share this article, leave comments, and explore other resources on our site to deepen their knowledge of cardiovascular health.