Student loans have become an integral part of the education system, helping millions of students worldwide achieve their academic dreams. Whether you're considering taking out a loan or already managing one, understanding the ins and outs of student loans is crucial. This guide will provide you with comprehensive information to make informed decisions about financing your education.
Education is a significant investment, and for many, student loans are the bridge to accessing quality higher education. However, navigating the world of student loans can be overwhelming due to the various options, terms, and repayment plans available. Understanding the terminology and processes involved can help you make smarter financial decisions.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of student loans, covering everything from the types of loans available to strategies for repayment. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer understanding of how student loans work and how to manage them effectively.
Read also:Imani Dukett Age Exploring The Life Career And Legacy Of A Rising Star
Table of Contents
- What Are Student Loans?
- Types of Student Loans
- Applying for Student Loans
- Understanding Interest Rates
- Repayment Options
- Loan Consolidation and Refinancing
- Managing Student Debt
- Federal vs. Private Student Loans
- Tax Implications of Student Loans
- Conclusion
What Are Student Loans?
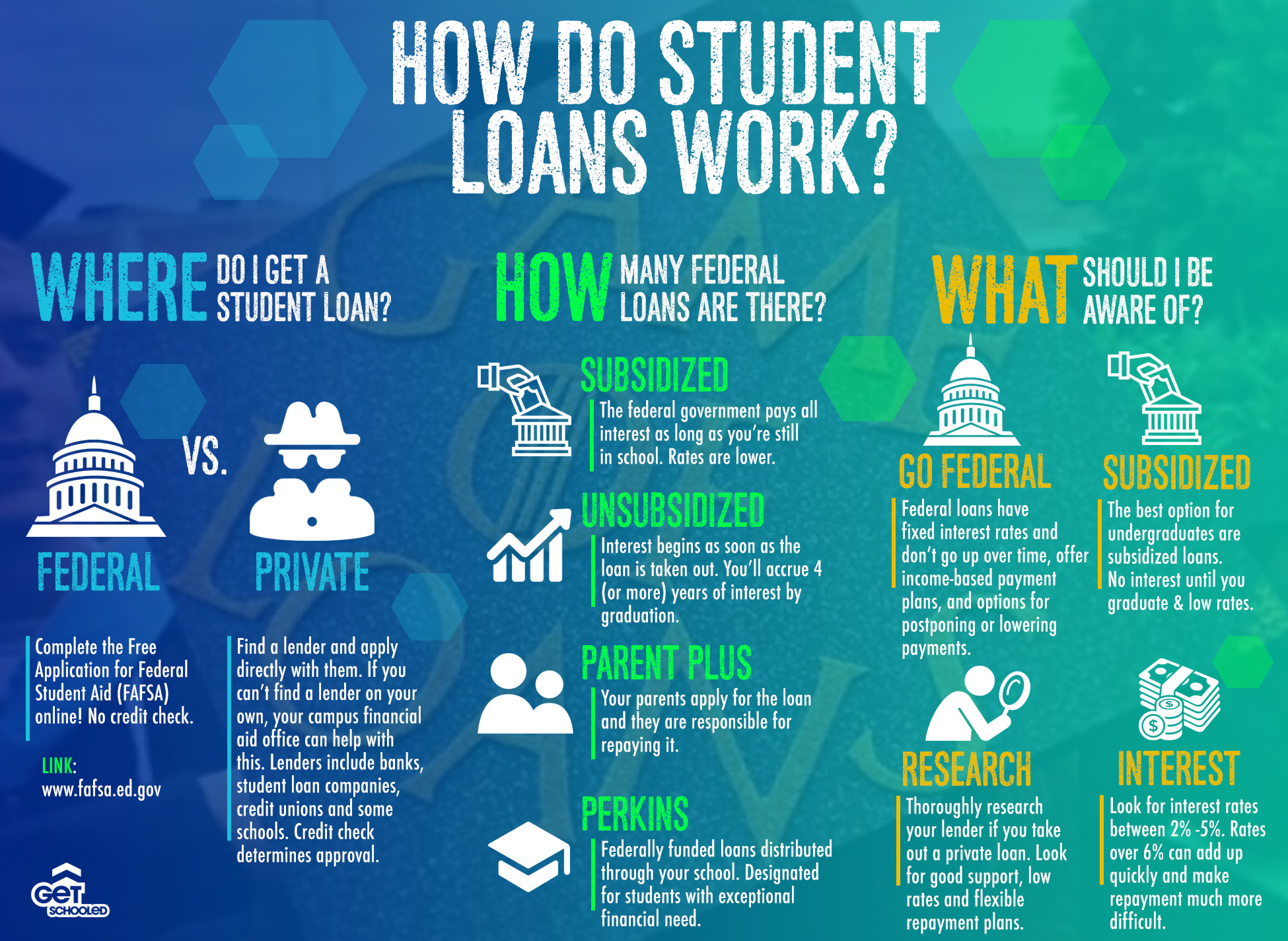
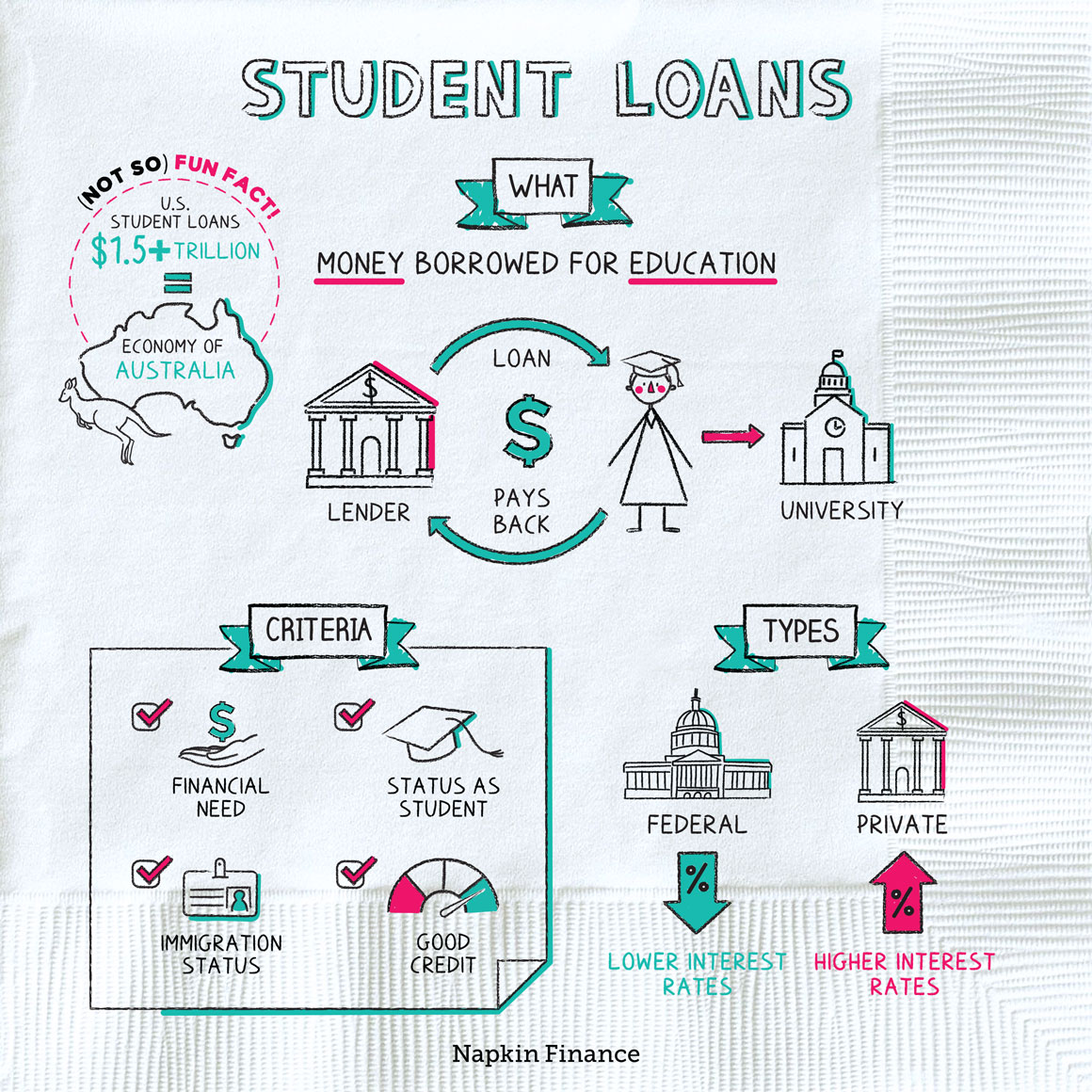
Student loans are financial resources provided to students to help them pay for their education-related expenses, including tuition fees, textbooks, and living costs. These loans are typically repaid after graduation, and they come with varying terms and conditions depending on the lender and type of loan.
One of the key aspects of student loans is that they are designed to be accessible to individuals who may not have the immediate financial means to pay for their education. However, it is essential to understand the implications of borrowing and the responsibilities that come with repaying these loans.
How Student Loans Work
Student loans function similarly to other types of loans. Borrowers apply for the loan, and if approved, the lender disburses the funds directly to the educational institution or to the borrower. Repayment typically begins after graduation, although some loans may require interest payments while the student is still in school.
Types of Student Loans
There are several types of student loans available, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Understanding the differences between these loans can help you choose the best option for your financial situation.
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. Department of Education and are generally considered more favorable than private loans due to their fixed interest rates and flexible repayment options. Types of federal student loans include:
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- Direct PLUS Loans
Private Student Loans
Private student loans are provided by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. They often have variable interest rates and less flexible repayment terms compared to federal loans. However, they can be a viable option for students who need additional funding beyond what federal loans offer.
Read also:Discover The Rise And Success Of Idol Yoo Yeon A Detailed Exploration
Applying for Student Loans
The process of applying for student loans involves several steps, starting with completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) for federal loans. For private loans, you will need to apply directly through the lender of your choice.
It is important to gather all necessary documents and information before starting the application process to ensure a smooth submission. This includes tax returns, financial aid letters, and any other required paperwork.
Tips for a Successful Application
To increase your chances of a successful application, consider the following tips:
- Submit your FAFSA as early as possible.
- Compare loan offers from multiple lenders.
- Understand the terms and conditions of each loan.
Understanding Interest Rates
Interest rates play a significant role in determining the total cost of your student loans. Federal loans typically offer fixed interest rates, while private loans may have variable rates that can fluctuate over time.
When comparing loans, it is crucial to consider not only the interest rate but also any fees associated with the loan, such as origination fees or prepayment penalties.
How Interest Rates Affect Repayment
Higher interest rates can significantly increase the amount you pay over the life of the loan. For example, a loan with a 6% interest rate will cost more in interest payments than a loan with a 3% interest rate over the same repayment period.
Repayment Options
Repayment plans for student loans vary depending on the type of loan and the borrower's financial situation. Federal loans offer several income-driven repayment plans that adjust monthly payments based on the borrower's income and family size.
Private loans typically have fixed repayment terms, but some lenders may offer deferment or forbearance options for borrowers experiencing financial hardship.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-driven repayment plans are designed to make loan repayment more manageable for borrowers with high debt relative to their income. These plans include:
- Income-Based Repayment (IBR)
- Pay As You Earn (PAYE)
- Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE)
Loan Consolidation and Refinancing
Loan consolidation and refinancing are options available to borrowers who want to simplify their repayment process or secure a lower interest rate. Consolidation combines multiple loans into a single loan, while refinancing involves replacing an existing loan with a new one, often with better terms.
It is important to weigh the pros and cons of consolidation and refinancing before making a decision, as these options may affect eligibility for certain benefits, such as loan forgiveness programs.
Benefits of Loan Consolidation
Consolidating your loans can offer several benefits, including:
- Lower monthly payments
- Simplified repayment process
- Potential for a lower interest rate
Managing Student Debt
Effectively managing student debt requires a proactive approach. Creating a budget, prioritizing payments, and exploring repayment assistance programs can help you stay on track with your financial goals.
It is also important to stay informed about any changes in loan policies or regulations that may affect your repayment plan.
Strategies for Paying Off Student Loans Faster
To pay off your student loans faster, consider the following strategies:
- Make extra payments when possible.
- Round up your monthly payments.
- Take advantage of employer tuition assistance programs.
Federal vs. Private Student Loans
Choosing between federal and private student loans depends on your financial needs and circumstances. Federal loans generally offer more borrower protections and flexible repayment options, while private loans may provide larger loan amounts or lower interest rates for borrowers with excellent credit.
It is essential to evaluate the pros and cons of each option before making a decision.
Key Differences Between Federal and Private Loans
Some key differences between federal and private student loans include:
- Interest rates
- Repayment options
- Borrower protections
Tax Implications of Student Loans
Student loans can have tax implications that affect your overall financial situation. Interest paid on student loans may be tax-deductible, which can reduce your taxable income and lower your tax liability.
It is important to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to fully understand the tax implications of your student loans.
Claiming the Student Loan Interest Deduction
To claim the student loan interest deduction, you must meet certain criteria, such as having a modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) below a specified threshold. Keeping accurate records of your loan payments can help you maximize this deduction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, student loans are a valuable resource for financing education, but they require careful consideration and management. By understanding the different types of loans, interest rates, repayment options, and tax implications, you can make informed decisions about your financial future.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on managing student loans and achieving financial independence.
Data source: U.S. Department of Education, Federal Student Aid