Exploring Indonesia: A Journey Through Culture, History, And Natural Beauty
Mar 21 2025
Indonesia is a country that offers a rich tapestry of cultural diversity, stunning landscapes, and a vibrant history that continues to shape its identity today. From the bustling streets of Jakarta to the serene beaches of Bali, Indonesia stands as a testament to the beauty of Southeast Asia. As the world's largest archipelago, the nation captivates travelers and researchers alike with its unique blend of traditions and modernity.
As one of the most populous countries in the world, Indonesia is a melting pot of ethnicities, languages, and religions. This diversity is what makes the nation so fascinating, offering something for everyone who visits or studies it. Whether you're exploring its historical landmarks, indulging in local cuisine, or simply enjoying the natural wonders, Indonesia provides endless opportunities for discovery.
For those interested in travel, culture, or even economic development, Indonesia remains a focal point. The country's strategic location, abundant natural resources, and dynamic economy make it a significant player on the global stage. In this article, we will delve into various aspects of Indonesia, uncovering its hidden gems and shedding light on what makes it such a remarkable destination.
Read also:Lawrence Jones Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Geography of Indonesia
- Indonesian Culture
- History of Indonesia
- Economy in Indonesia
- Tourism in Indonesia
- Environmental Challenges
- Education System in Indonesia
- Politics and Governance
- Technology and Innovation
- Conclusion
Geography of Indonesia
Indonesia is an archipelago located between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, consisting of over 17,000 islands. It spans across an area of approximately 1.9 million square kilometers, making it the world's largest island country. The country is geographically divided into several regions, including Sumatra, Java, Borneo, Sulawesi, and Papua.
The geography of Indonesia plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, biodiversity, and economic activities. The equatorial location results in a tropical climate with high humidity and rainfall throughout the year. This climate supports lush rainforests, which are home to diverse flora and fauna, including endangered species such as orangutans and Komodo dragons.
Key Geographic Features
- Mountains: Indonesia has numerous volcanic mountains, with Mount Semeru being the highest peak.
- Rivers: Major rivers like the Kapuas and Mahakam provide essential water resources for agriculture and transportation.
- Coastlines: With over 54,000 kilometers of coastline, Indonesia boasts some of the world's most beautiful beaches.
According to the World Bank, Indonesia's geographic position makes it vulnerable to natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. However, it also provides opportunities for marine tourism and fishing industries.
Indonesian Culture
Culture in Indonesia is a vibrant mosaic of traditions, languages, and art forms. With over 300 ethnic groups and more than 700 languages, the cultural diversity of Indonesia is unparalleled. The country's cultural heritage is reflected in its music, dance, cuisine, and festivals.
Traditional dances like the Balinese Legong and Javanese Wayang Kulit (shadow puppet theater) are celebrated worldwide. Indonesian music, characterized by the use of gamelan instruments, adds to the rich tapestry of cultural expressions. Furthermore, Indonesian cuisine, which includes dishes like Nasi Goreng, Satay, and Rendang, has gained international recognition.
Key Cultural Elements
- Religion: Indonesia is the world's most populous Muslim-majority country, but it also embraces Christianity, Hinduism, Buddhism, and traditional beliefs.
- Festivals: Events like Nyepi (Day of Silence) in Bali and Independence Day celebrations showcase the nation's cultural vibrancy.
- Textiles: Batik, a traditional fabric-making technique, is recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage.
History of Indonesia
The history of Indonesia dates back thousands of years, with evidence of human habitation found in the archipelago from as early as the Paleolithic era. Over the centuries, Indonesia has been influenced by various civilizations, including the Hindu-Buddhist kingdoms of Srivijaya and Majapahit, followed by the Islamic Sultanates and European colonial powers.
Read also:George Clooney Death Debunking The Myths And Exploring The Truth
Indonesia declared independence on August 17, 1945, following the end of Japanese occupation during World War II. However, it took several years of struggle before the country achieved full sovereignty in 1949. Since then, Indonesia has undergone significant political and social transformations, including the transition to democracy in the late 20th century.
Historians often highlight the importance of Indonesia's strategic location in facilitating trade and cultural exchange throughout history. The Spice Islands, located in modern-day Maluku, were a major attraction for traders from around the world, contributing to the country's historical significance.
Economy in Indonesia
Indonesia's economy is one of the largest in Southeast Asia, driven by a combination of agriculture, manufacturing, and services sectors. The country is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, and minerals, which contribute significantly to its GDP. In recent years, Indonesia has made strides in reducing poverty and improving infrastructure, although challenges remain.
As of 2023, Indonesia's GDP ranks among the top 20 globally, with a focus on diversifying its economic base. The government has implemented policies to attract foreign investment and promote small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Tourism, digital technology, and renewable energy are emerging as key growth sectors.
Economic Challenges
- Inequality: Despite economic growth, income inequality remains a pressing issue.
- Infrastructure: Improving transportation networks and digital connectivity is essential for sustainable development.
- Environmental Impact: Balancing economic growth with environmental conservation poses a significant challenge.
Tourism in Indonesia
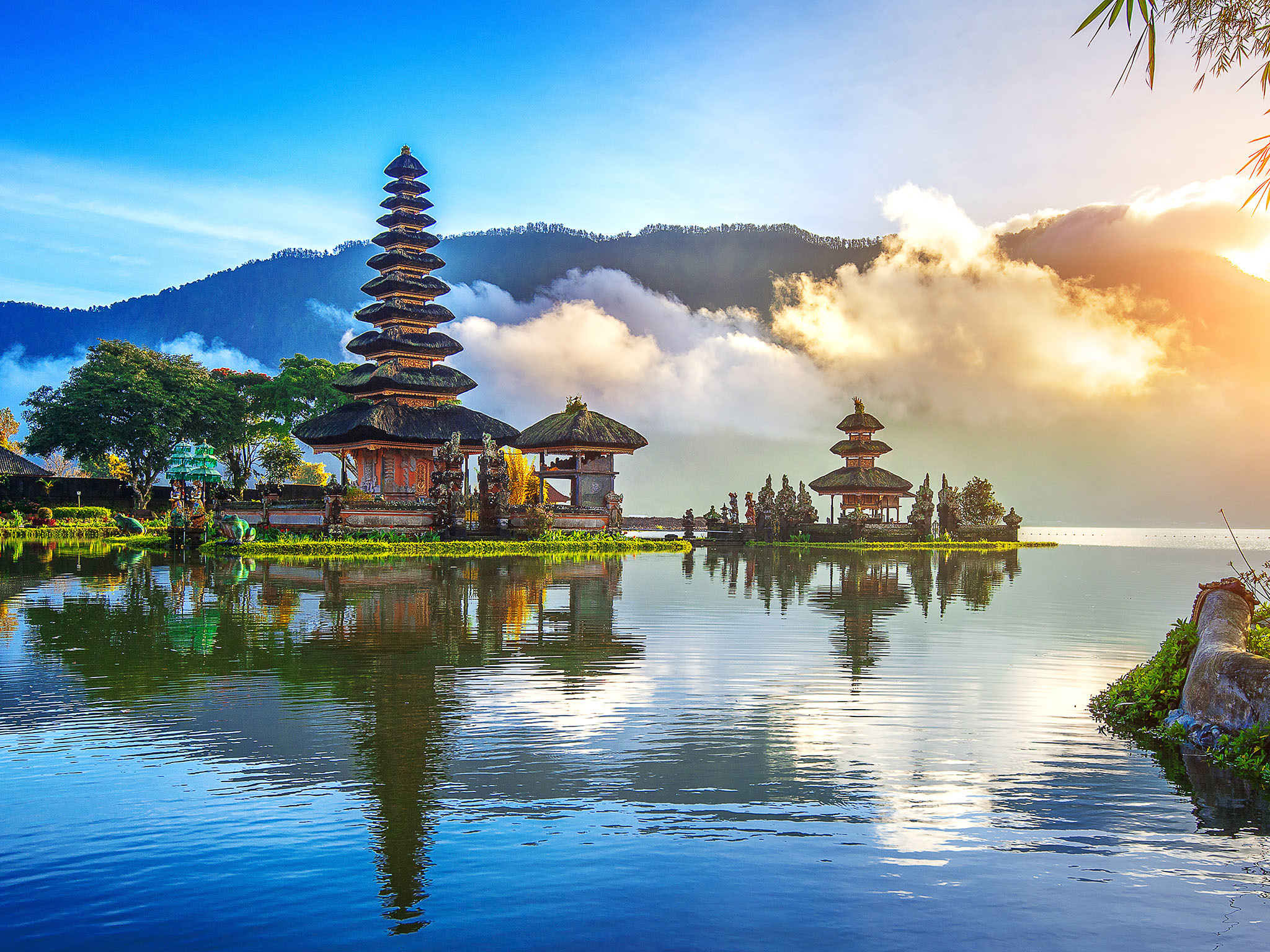
Tourism is a vital component of Indonesia's economy, attracting millions of visitors each year. The country's natural beauty, cultural heritage, and hospitality make it a popular destination for both domestic and international travelers. Popular tourist spots include Bali, Lombok, Komodo Island, and Borobudur Temple.
Indonesia's tourism industry is supported by a range of activities, from adventure sports like diving and hiking to cultural experiences such as attending traditional ceremonies. The government has prioritized infrastructure development, including airports and hotels, to enhance the tourist experience.
Top Tourist Destinations
- Bali: Known for its beaches, temples, and vibrant arts scene.
- Raja Ampat: Offers world-class diving opportunities with stunning marine life.
- Borobudur: The largest Buddhist temple in the world, attracting history enthusiasts.
Environmental Challenges
Indonesia faces significant environmental challenges due to its vast biodiversity and rapid economic development. Deforestation, pollution, and climate change are among the most pressing issues. The country's rainforests, which are critical for global carbon absorption, are under threat from illegal logging and agricultural expansion.
Efforts to address these challenges include reforestation programs, protected area management, and international partnerships. The Indonesian government has committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices across various sectors.
Solutions for Environmental Sustainability
- Renewable Energy: Investing in solar, wind, and hydroelectric power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts to ensure long-term success.
- Policy Implementation: Strengthening regulations to combat illegal activities and promote eco-friendly practices.
Education System in Indonesia
Education in Indonesia is a priority for the government, with efforts to improve access and quality at all levels. The education system consists of primary, secondary, and tertiary education, with compulsory schooling for children aged 7 to 15. Despite progress, challenges such as disparities in access and teacher quality persist.
Higher education institutions in Indonesia, including the University of Indonesia and Bandung Institute of Technology, are recognized for their academic excellence. The government has also introduced scholarship programs to support talented students from disadvantaged backgrounds.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Infrastructure: Building more schools and improving facilities in remote areas is crucial.
- Curriculum Development: Aligning education with industry needs to prepare students for the future job market.
- Technological Integration: Incorporating digital tools in classrooms to enhance learning experiences.
Politics and Governance
Indonesia operates as a presidential republic, with a president serving as both head of state and government. The country has undergone significant political reforms since the fall of the New Order regime in 1998, transitioning to a more democratic system. The Indonesian Parliament, known as the People's Consultative Assembly, plays a key role in shaping national policies.
Challenges in governance include corruption, regional autonomy issues, and ensuring accountability. However, Indonesia has made progress in strengthening its institutions and promoting transparency. Civil society and media play important roles in monitoring government actions and advocating for reform.
Key Political Developments
- Decentralization: Granting more power to local governments to improve service delivery.
- Anti-Corruption Efforts: Strengthening legal frameworks to combat corruption at all levels.
- Election Processes: Conducting free and fair elections to ensure democratic representation.
Technology and Innovation
Technology is transforming Indonesia's landscape, with rapid advancements in digital infrastructure, fintech, and e-commerce. The country's young and tech-savvy population has driven the growth of startups and innovation hubs. Platforms like Gojek and Tokopedia have become household names, revolutionizing transportation and retail sectors.
The government has launched initiatives to support technological development, including smart city projects and digital literacy programs. Collaboration with international partners is also playing a crucial role in enhancing Indonesia's technological capabilities.
Future Trends in Technology
- Artificial Intelligence: Implementing AI solutions in healthcare, education, and agriculture.
- Cybersecurity: Strengthening measures to protect sensitive data and infrastructure.
- Green Technology: Promoting sustainable practices through renewable energy and eco-friendly innovations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Indonesia stands as a remarkable country with a rich cultural heritage, diverse geography, and dynamic economy. From its historical significance to its current role on the global stage, Indonesia continues to evolve and adapt to modern challenges. The nation's commitment to sustainability, education, and technological innovation ensures a promising future for its people.
We invite you to explore more about Indonesia by sharing this article with your friends or leaving a comment below. Your feedback is valuable in helping us improve and provide even more insightful content. For further reading, check out our other articles on Southeast Asian countries and their unique contributions to the world.