NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 Re-Entry And Splashdown: A Triumph In Space Exploration
Mar 21 2025
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission has marked a significant milestone in the history of space exploration. The successful re-entry and splashdown of the Crew Dragon spacecraft demonstrate the remarkable progress in human spaceflight capabilities. This mission not only highlights the collaboration between NASA and SpaceX but also underscores the importance of sustainable space travel for future missions.
Space exploration has always been a beacon of human ingenuity and ambition. NASA’s partnership with SpaceX represents a new era in space travel, where private companies collaborate with government agencies to push the boundaries of what is possible. The Crew-9 mission exemplifies this synergy, showcasing the advancements in technology and innovation.
As we delve deeper into the details of the mission, it becomes evident that the re-entry and splashdown phases are among the most critical and challenging. These phases require precise planning, cutting-edge technology, and unwavering dedication from the teams involved. Let’s explore the intricacies of this mission and its implications for the future of space exploration.
Read also:Unveiling The Extraordinary Life Of John Duff Dick A Comprehensive Biography
Table of Contents
- Mission Overview: NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9
- The Crew Dragon Technology: A Breakthrough in Spacecraft Design
- Understanding the Re-Entry Process
- Splashdown Details: Ensuring Crew Safety
- Key Objectives of the Crew-9 Mission
- Challenges Faced During the Mission
- Future Implications for Space Exploration
- Data and Statistics: Mission Highlights
- The NASA-SpaceX Collaboration: A Model for Success
- Conclusion: Celebrating a Milestone in Space Exploration
Mission Overview: NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission is part of the Commercial Crew Program, a groundbreaking initiative aimed at transporting astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS). The mission, which launched in early 2024, involved a team of four astronauts who conducted critical research and maintenance activities aboard the ISS. The re-entry and splashdown phase marked the culmination of their successful mission.
Key Features of the Mission
- Duration: Approximately six months in space
- Primary Objective: Conducting scientific experiments and maintaining ISS operations
- Spacecraft: SpaceX Crew Dragon
- Launch Site: Kennedy Space Center, Florida
The Crew-9 mission highlights the growing reliance on commercial partners like SpaceX to support NASA’s goals in space exploration. This collaboration not only reduces costs but also accelerates the development of new technologies.
The Crew Dragon Technology: A Breakthrough in Spacecraft Design
The SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft is a testament to modern engineering and innovation. Designed specifically for human spaceflight, the Crew Dragon offers several advantages over traditional spacecraft:
- Advanced propulsion systems for precise orbital maneuvers
- State-of-the-art life support systems to ensure crew safety
- Autonomous docking capabilities for seamless ISS operations
- Enhanced thermal protection for safe re-entry
These features make the Crew Dragon one of the most advanced spacecraft in operation today. Its ability to withstand the harsh conditions of re-entry and splashdown is a testament to its robust design and engineering excellence.
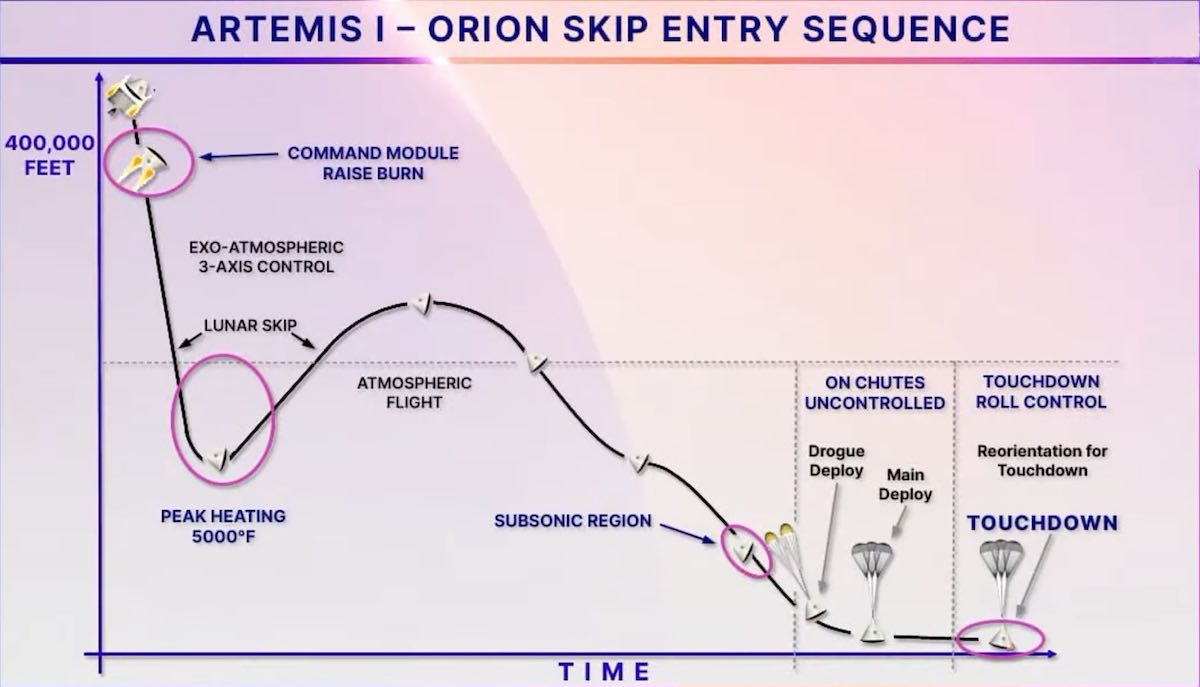
Understanding the Re-Entry Process
The re-entry phase of the Crew-9 mission is a critical and complex operation. As the Crew Dragon descends through Earth’s atmosphere, it must withstand temperatures exceeding 3,000°F and decelerate from speeds of over 17,000 mph. This process involves several key stages:
Read also:Who Is Tim Kennedy Married To Exploring The Life And Relationships Of The Renowned Fighter
Stages of Re-Entry
- Deployment of drogue parachutes to stabilize the spacecraft
- Deployment of main parachutes to further reduce speed
- Final descent and splashdown in the Atlantic Ocean
Each stage requires precise timing and coordination to ensure the safety of the crew and the integrity of the spacecraft. The success of this phase is a testament to the meticulous planning and execution by the mission teams.
Splashdown Details: Ensuring Crew Safety
The splashdown of the Crew Dragon spacecraft is a carefully orchestrated event. The location of the splashdown site is chosen based on weather conditions, sea state, and proximity to recovery vessels. Upon splashdown, the recovery team quickly moves into action to secure the spacecraft and extract the crew.
Recovery Process
- Assessment of the spacecraft’s condition
- Medical evaluations of the crew
- Transportation of the crew to shore
The recovery process is a testament to the collaboration between NASA, SpaceX, and various support teams. It ensures the safe return of the astronauts and the preservation of valuable scientific data collected during the mission.
Key Objectives of the Crew-9 Mission
The Crew-9 mission was designed to achieve several key objectives, including:
- Conducting scientific experiments aboard the ISS
- Maintaining and upgrading ISS systems
- Testing new technologies for future missions
These objectives are crucial for advancing our understanding of space and preparing for long-duration missions to destinations like the Moon and Mars. The success of the Crew-9 mission demonstrates the importance of sustained human presence in space.
Challenges Faced During the Mission
Despite its success, the Crew-9 mission faced several challenges, including:
- Technical issues with spacecraft systems
- Unpredictable weather conditions during launch and splashdown
- Complexity of scientific experiments
Overcoming these challenges required the expertise and dedication of the mission teams. Their ability to adapt and respond to unexpected situations highlights the resilience and ingenuity of the space exploration community.
Future Implications for Space Exploration
The success of the Crew-9 mission has significant implications for the future of space exploration. It paves the way for more ambitious missions, including:
- Artemis Program: Returning humans to the Moon
- Mars Exploration: Preparing for human missions to the Red Planet
- Commercial Space Travel: Expanding opportunities for private citizens
These initiatives will build on the lessons learned from the Crew-9 mission and leverage the advancements in technology and collaboration it has fostered.
Data and Statistics: Mission Highlights
The Crew-9 mission produced several noteworthy statistics, including:
- More than 200 scientific experiments conducted aboard the ISS
- Successful completion of over 1,000 hours of research activities
- Precision splashdown within 1 mile of the target location
These statistics underscore the mission’s success and its contribution to advancing scientific knowledge and technological capabilities.
The NASA-SpaceX Collaboration: A Model for Success
The partnership between NASA and SpaceX represents a new paradigm in space exploration. By leveraging the strengths of both organizations, this collaboration has achieved remarkable successes, including:
- Reduction in costs associated with space travel
- Acceleration of technology development
- Enhancement of mission capabilities
This model of collaboration serves as an inspiration for future partnerships in space exploration and beyond.
Conclusion: Celebrating a Milestone in Space Exploration
NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission has set a new standard for human spaceflight. The successful re-entry and splashdown of the Crew Dragon spacecraft demonstrate the incredible achievements possible through collaboration, innovation, and dedication. As we look to the future, the lessons learned from this mission will guide us toward even greater accomplishments in space exploration.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights about the Crew-9 mission in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to learn more about the exciting world of space exploration. Together, let’s celebrate the milestones that bring us closer to understanding the vast universe beyond our planet.